The management of water in urban environments is increasingly vital as cities expand and climate patterns shift. One innovative solution to managing water runoff while supporting local ecosystems is the use of drainage cells. In particular, the concept of a Drain cell in India has gained traction as urban planners and environmentalists strive to create sustainable systems that not only mitigate flooding but also enhance ecological balance. This article explores how drainage cells function within local ecosystems, their installation process, and their benefits to both urban areas and natural habitats.
Understanding Drainage Cells
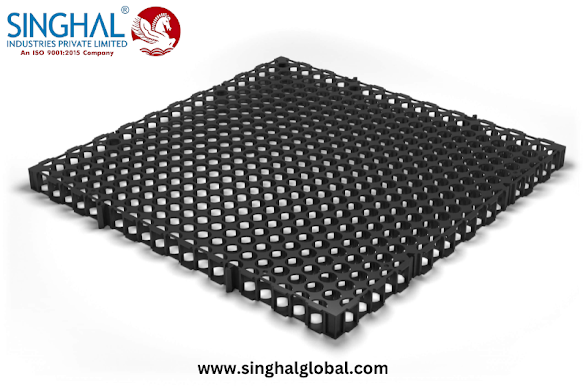
A drain cell is a modular system designed to manage stormwater runoff effectively. Made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE), these cells create void spaces that allow water to flow through while retaining soil and vegetation. This innovative structure can significantly reduce surface runoff, which often leads to urban flooding, erosion, and water pollution. By facilitating better water management, drain cells support local ecosystems by promoting groundwater recharge and maintaining hydrological balance.
Drain Cell Installation: A Crucial Process
The drainage cell installation process involves several key steps to ensure optimal performance and integration with existing systems. Initially, site assessments are conducted to evaluate soil conditions, existing drainage patterns, and the surrounding environment. This helps in determining the appropriate size and configuration of the drainage cells. The next step involves excavation, where a trench is dug to accommodate the cells.
After the trench is prepared, a layer of geotextile fabric is often placed at the bottom to prevent soil intrusion into the cells. The cells are then installed, usually in a grid pattern, to maximize their effectiveness. Once the cells are in place, they are covered with additional layers of soil and vegetation. This installation not only enhances water management but also promotes biodiversity, as native plants can thrive in the area.
Ecological Benefits of Drainage Cells
The integration of Drain cell mat into local ecosystems yields numerous ecological benefits. These mats, which often consist of interconnected drainage cells, create a habitat for various organisms while facilitating the absorption of excess water. One of the primary advantages of using drain cells is their ability to reduce the volume of stormwater runoff. By capturing and infiltrating water, they help recharge groundwater aquifers, which is essential for maintaining healthy water levels in nearby rivers and streams.
Moreover, drain cells play a crucial role in filtering pollutants from stormwater. As water passes through the soil and vegetation layers above the drainage cells, sediments and contaminants are naturally removed. This not only improves water quality but also supports aquatic ecosystems by ensuring that clean water enters local waterways.
The Impact on Local Biodiversity
The installation of drainage cells can significantly enhance local biodiversity. By creating a habitat for flora and fauna, these systems foster an environment where various species can thrive. Native plants, which are typically chosen for their resilience and ecological compatibility, attract pollinators such as bees and butterflies. Additionally, the retention of water in the drainage cells provides a suitable environment for amphibians and other small wildlife.
In urban settings, the presence of green spaces created by drain cell systems helps mitigate the urban heat island effect, contributing to cooler temperatures and improved air quality. This interplay between man-made systems and natural ecosystems highlights the potential for sustainable urban development that prioritizes biodiversity.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits of drainage cells are significant, there are also challenges associated with their installation and maintenance. In some areas, particularly in India, the soil composition may not always be conducive to effective drainage. Clay-heavy soils, for example, can impede water infiltration, necessitating additional engineering solutions.
Maintenance is another critical aspect of ensuring the effectiveness of drainage cell systems. Regular inspections are essential to prevent blockages caused by sediment buildup or plant overgrowth. Without proper maintenance, the cells may become less effective over time, undermining their intended benefits.
Case Studies: Successful Implementations
Several cities in India have successfully implemented drainage cell systems, showcasing their potential to enhance local ecosystems. For instance, in Bangalore, the installation of drainage cells has been instrumental in managing stormwater runoff during the monsoon season. The integration of these systems with existing lakes and wetlands has improved water quality and provided habitat for various species.
Similarly, in Mumbai, urban planners have embraced drainage cell technology to mitigate flooding risks in densely populated areas. By creating green spaces around the cells, they have also enhanced the city’s aesthetic appeal while supporting local biodiversity.
Future Directions
As climate change continues to pose challenges to urban infrastructure, the importance of drainage cells in maintaining ecological balance cannot be overstated. Future developments should focus on enhancing the design and functionality of these systems to ensure they meet the needs of both urban areas and surrounding ecosystems.
Research into innovative materials and construction techniques could lead to more efficient drainage cell systems that better withstand extreme weather events. Furthermore, integrating smart technologies for monitoring water levels and quality can optimize the performance of drainage cells and ensure that they adapt to changing environmental conditions.
Conclusion
The interplay between drainage cells and local ecosystems presents a unique opportunity to create sustainable urban environments. By effectively managing stormwater, enhancing biodiversity, and improving water quality, drainage cells serve as a vital component of modern urban planning. As cities in India and beyond continue to grapple with the challenges posed by urbanization and climate change, the implementation of drainage cells represents a promising path forward, balancing the needs of infrastructure and the environment.
By embracing innovative solutions like drain cell mats and prioritizing thoughtful Drainage cell installation, communities can create resilient ecosystems that support both people and nature. The future of urban water management lies in recognizing and enhancing these complex interrelationships, ensuring that our cities can thrive while preserving the natural world around us.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How do drainage cells contribute to environmental sustainability?
Drainage cells promote environmental sustainability by improving water quality, reducing flooding, and supporting biodiversity. Their ability to filter pollutants from stormwater runoff helps protect local waterways and ecosystems.
Are there any maintenance requirements for drainage cells?
Yes, regular maintenance is necessary to ensure the effectiveness of drainage cells. This includes inspecting for clogs, cleaning sediment buildup, and checking for damage to the cells.
Can drainage cells be used in areas with heavy clay soils?
While drainage cells can still be used in areas with heavy clay soils, their effectiveness may be limited. It is crucial to conduct site assessments and consider additional drainage solutions if soil permeability is a concern.
Comments
Post a Comment